PCB design tips and tricks
1、How to choose a PCB board?
The PCB board must be selected to meet the design requirements and to achieve a balance between mass production and cost. Design requirements include both electrical and mechanical components. Usually in the design of very high-speed PCB boards (greater than GHz frequency) when the material issues will be more important. For example, with the FR-4 material now commonly used, dielectric loss at frequencies of several GHz can have a significant impact on signal attenuation and may not be suitable. In electrical terms, attention should be paid to the dielectric constant and the dielectric loss at the frequency for which it is designed.
2、How to avoid high frequency interference?
The basic idea of avoiding high frequency interference is to minimise the interference of the electromagnetic field of the high frequency signal, also known as crosstalk. This can be achieved by increasing the distance between the high speed signal and the analogue signal, or by adding ground guard/shunt traces next to the analogue signal. Note also the noise interference from digital to analogue ground.
3、How to solve the signal integrity problem in high speed design?
Signal integrity is basically a matter of impedance matching. The factors that affect impedance matching are the architecture and output impedance of the signal source, the characteristic impedance of the alignment, the characteristics of the load side, the topology of the alignment and so on. The solution is to terminate and adjust the topology of the cable.
4. How is the differential wiring method implemented?
There are two points to note when wiring differential pairs. One is that the two lines should be as long as possible and the other is that the spacing between the two lines (which is determined by the differential impedance) should remain constant, i.e. parallel. There are two types of parallelism, one for two lines running on the same alignment layer (side-by-side), and one for two lines running on two adjacent layers (over-under). Generally the former side-by-side implementation is more often.
5, for only one output of the clock signal line, how to achieve a differential distribution line?
To use a differential distribution line it makes sense that the source and the receiver are also differential signals. So for only one output of the clock signal is not possible to use the differential distribution line.
6. Can a matching resistor be added between the differential pairs at the receiving end?
The matching resistor between the differential pairs at the receiving end is usually added and its value should be equal to the differential impedance value. This way the signal quality will be better.
7、Why should the differential pairs be wired close together and parallel?
Differential pairs should be wired close together and parallel to each other. The reason for this is that the spacing affects the differential impedance, which is an important parameter in the design of a differential pair. Parallelism is also required to maintain the consistency of the differential impedance. If the two lines are far apart and close together, the differential impedance will be inconsistent and this will affect signal integrity and timingdelay.
8. How to deal with some theoretical conflicts in practical wiring
1. Basically, it is right to separate the analogue/digital ground. It is important that the signal routing does not cross the split (moat) and that the return current path between the power supply and the signal does not become too large. 2.
The crystal is an analogue positive feedback oscillation circuit, to have a stable oscillation signal, it must meet the loop gain and phase specification, and this analogue signal oscillation specification is susceptible to interference, even with ground guard traces may not be able to completely isolate the interference. Even adding ground guard traces may not be able to isolate the interference completely. Furthermore, noise on the ground plane can affect the positive feedback oscillation circuit if it is too far away. Therefore, it is important to keep the crystal and the chip as close as possible to each other. 3.
It is true that there are many conflicts between high-speed cabling and EMI requirements. However, the basic principle is that the resistor-capacitor or ferritebead added by EMI must not cause some electrical characteristics of the signal to fail to meet the specification. Therefore, it is best to use the arrangement of alignment and PCB lamination techniques to solve or reduce the EMI problem, such as high-speed signal to the inner layer. Finally only with resistors capacitors or ferrite bead way, to reduce the harm to the signal.
9, how to solve the contradiction between manual and automatic routing of high-speed signals?
Nowadays, most of the stronger wiring software has automatic wiring devices that set constraints to control the winding method and the number of vias. The capability of the winding engines and the constraints set by the EDA companies sometimes vary greatly. For example, whether there are sufficient constraints to control the way the serpentine is wound, the spacing between differential pairs, etc. This can affect the alignment of the autowire. This has an impact on whether the automatic wiring produces the desired alignment. In addition, the ease of manual routing is absolutely dependent on the capability of the winding engine. For example, the ability to push and squeeze the wires, the ability to push and squeeze through holes, or even the ability to push and squeeze the wires against the copper. Therefore, the solution is to choose a wiring machine with a strong winding engine.
10、About test coupon.
The test coupon is used to measure the characteristic impedance of the PCB produced by the TDR (Time Domain Reflectometer) to meet the design requirements. Generally to control the impedance of a single line and differential pairs of two cases. Therefore, the width and spacing of the lines on the test coupon (in the case of differential pairs) must be the same as the lines to be controlled. The most important thing is the position of the grounding point during the measurement. In order to reduce the inductance of the ground lead (ground lead), the TDR probe (probe) grounding place is usually very close to the measurement of the signal (probe tip), so the point on the test coupon to measure the signal and the grounding point of the distance and the way to match the probe used.
11、In the high-speed PCB design, the blank area of the signal layer can be coppered, but how should the coppering of multiple signal layers be distributed in terms of ground and power supply?
Generally in the blank area of the copper laying in the vast majority of cases is grounded. However, when laying copper next to high-speed signal lines, care should be taken to ensure that the copper is placed at a distance from the signal line, as the copper laid will reduce the characteristic impedance of the line a little. Care should also be taken not to affect the characteristic impedance of its layer, for example in the structure of the dual stripline.
12. Is it possible to calculate the characteristic impedance of the signal lines above the power plane using the microstrip line model? Can the signal between the power and ground planes be calculated using the ribbon line model?
Yes, both the power and ground planes must be considered as reference planes when calculating the characteristic impedance. For example, for a four-layer board: top layer - power layer - ground layer - bottom layer, the model for the characteristic impedance of the top layer is a microstrip line model with the power plane as the reference plane.
13、Can automatic software generation of test points on high-density printed circuit boards normally meet the test requirements of high-volume production?
Generally, whether the software automatically generates test points to meet test requirements depends on whether the specifications for adding test points meet the requirements of the test machine. In addition, if the alignment is too dense and the specifications for adding test points are relatively strict, there may be no way to automatically add test points to each section of the line, but of course, you will need to manually fill in the places to be tested.
14、Will adding test points affect the quality of the high-speed signal?
It depends on how the test points are added and how fast the signal is. Basically an additional test point (without using the existing via or DIP pin as a test point) can be added to the wire or a small section of wire can be pulled out of the wire. The former is equivalent to adding a very small capacitor to the line, while the latter is an additional branch. Both of these situations will affect the high speed signal to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the frequency speed and the edge rate of the signal. The magnitude of the effect can be determined by simulation. In principle, the smaller the test point, the better (of course, to meet the requirements of the test equipment), the shorter the branch the better.
15、Several PCBs form a system, how should the ground between each board be connected?
Each PCB board connected to each other between the signal or power in the action, for example, A board has power or signal to B board, there must be an equal amount of current from the ground back to the A board (this is Kirchoff current law). The current on this ground level will find the lowest impedance and flow back. Therefore, the number of pins allocated to the ground layer at each interface, whether for power or signal interconnection, should not be too small in order to reduce the impedance and thus reduce the noise on the ground layer. In addition, you can also analyse the whole current loop, especially the part with higher current, and adjust the ground layer or ground connection to control the way the current goes (for example, create a low impedance at a certain place, so that most of the current goes from this place), to reduce the impact on other more sensitive signals.
16, can introduce some foreign technical books and materials on high-speed PCB design?
Nowadays, high-speed digital circuits are used in communication networks and computers and other related fields. In communication networks, PCBs have been operating at frequencies above and below GHz, with as many as 40 layers as far as I know. Computer-related applications are also due to chip advances, whether it is a general PC or server (Server), the maximum operating frequency on the board has also reached 400MHz (such as Rambus) or more. In response to these high speed and high density alignments, blind/buried vias, mircrovias and build-up processes are increasingly in demand. All these design requirements are available from manufacturers in large quantities.
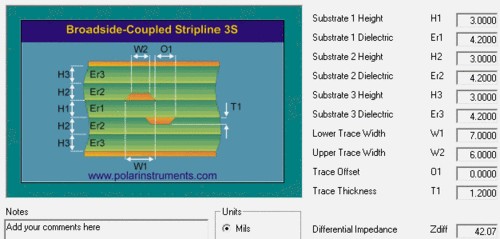
17. Two commonly referenced characteristic impedance formulas are
a. Microstrip Z={87/[sqrt(Er+1.41)]}ln[5.98H/(0.8W+T)] where W is the line width, T is the thickness of the copper skin of the alignment, H is the distance from the alignment to the reference plane and Er is the dielectric constant of the PCB material (dielectric constant). This formula must be applied when 0.1<(W/H)<2.0 and 1<(Er)<15.
b. Stripline Z=[60/sqrt(Er)]ln{4H/[0.67π(T+0.8W)]} where H is the distance between the two reference planes and the alignment is in the middle of the two reference planes.
the middle of the plane. This formula must be applied if W/H < 0.35 and T/H < 0.25.
18、Can I add a ground line in the middle of a differential signal line?
The middle of the differential signal is generally not allowed to add a ground line. This is because the most important point of the application principle of differential signals is to make use of the benefits brought by the mutual coupling (coupling) between differential signals, such as flux cancellation, noise immunity and so on. If a ground is added in the middle, the coupling effect will be destroyed.
19、Do I need special design software and specifications for rigid-flexible board design? Where in China can I get this type of board processed?
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) can be designed using the same software used to design PCBs in general. You can also use the same Gerber format for FPC manufacturers. As the manufacturing process is different from that of a normal PCB, each manufacturer has its own restrictions on minimum line width, minimum line spacing and minimum hole diameter (via) depending on their manufacturing capabilities. In addition to this, the flex PCB can be reinforced by laying some copper skin at the turnaround points. As for the manufacturer of the production can be found online "FPC" as a keyword query should be able to find.
20、What is the principle of proper selection of PCB and shell grounding points?
The principle of choosing a PCB and housing ground point is to use the chassis ground to provide a low impedance path for the return current (return current) and to control the path of this return current. For example, usually in the vicinity of high-frequency devices or clock generators can be fixed with screws to connect the ground layer of the PCB with the chassis ground to minimise the overall current circuit area, also to reduce electromagnetic radiation.
21, the circuit board DEBUG should start from those aspects?
In the case of digital circuits, first determine three things in order: 1.
1. make sure that all power supply values are sized as required by the design. Some systems with multiple power supplies may require that some of the power supplies
1. make sure that all power supply values are in the order required by the design.
2. verify that all clock signal frequencies are operating correctly and that there are no non-monotonic issues on the signal edges. 3.
3. make sure that the reset signal meets the specification.
If all this is correct, the chip should send the first cycle signal. Next, debug the system according to its operating principle and bus
The next step is to debug according to the system operating principle and the bus protocol.
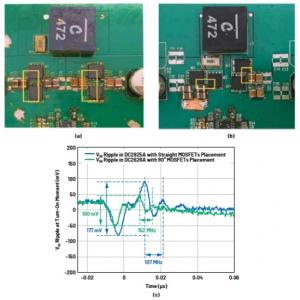
22, in the case of a fixed board size, if the design needs to accommodate more functions, it is often necessary to increase the density of the PCB alignment, but this may lead to increased interference with each other, while the alignment is too thin to reduce the impedance, please experts in high-speed (> 100MHz) high-density PCB design skills?
When designing high speed high density PCBs, crosstalk interference is really something to pay special attention to, as it has a great impact on timing and signal integrity. The following are a few areas of concern.
1. Control the continuity and matching of the characteristic impedance of the alignments.
2. The size of the cable spacing. Generally, the spacing is twice the width of the line. Simulations can be used to see the effect of spacing on timing and signal integrity and to find the minimum tolerable spacing. The results may vary from chip to chip.
3. Choose the appropriate termination method.
4. Avoid having alignments on the top and bottom of two adjacent layers in the same direction, or even having alignments that overlap on the top and bottom, as this crosstalk is greater than if the alignments were on the same layer and adjacent.
5. Use blind/buried via to increase the routing area. However, the cost of producing the PCB increases. In practice it is difficult to achieve perfect parallelism and equal length, but it is important to try to do so. In addition, differential termination and common mode termination can be reserved to mitigate the effects on timing and signal integrity.
23. LC circuits are often used for filtering at analogue power supplies. But why is LC sometimes less effective than RC filtering?
The comparison between LC and RC filtering must take into account the frequency band to be filtered out and the appropriateness of the choice of inductor value. This is because the reactance of an inductor is related to its value and frequency. If the noise frequency of the power supply is low, and the inductor value is not large enough, then the filtering effect may not be as good as RC, but the price to be paid for using RC filtering is that the resistor itself will consume energy and be less efficient, and attention should be paid to the power that the selected resistor can withstand.
24、What is the method of selecting inductor and capacitor values for filtering?
In addition to the frequency of the noise to be filtered out, the choice of inductor value should also take into account the responsiveness of the transient current. If there is a chance that the output side of the LC will need to output a large current instantaneously, the inductor value will be too large and will prevent the large current from flowing through the inductor, increasing the ripple noise. The value of the capacitance is related to the size of the ripple noise specification that can be tolerated. The smaller the ripple noise requirement, the larger the capacitance value. The ESR/ESL of the capacitor also has an influence. In addition, if the LC is placed at the output of a switching regulation power supply, attention must be paid to the effect of the pole/zero generated by this LC on the stability of the negative feedback control loop.
25、How can I achieve the EMC requirements without causing too much cost pressure?
The increased cost of EMC on pcb boards is usually due to the increased number of ground layers to enhance the shielding effect and the addition of high frequency harmonic suppression devices such as ferritebead and choke. In addition to this, it is often necessary to use other shielding structures to make the whole system pass the EMC requirements. The following are just a few design tips for PCB boards to reduce the electromagnetic radiation effects generated by the circuit.
1. Use devices with a slower signal slope (slew rate) as far as possible to reduce the high frequency component of the signal. 2, pay attention to the placement of high-frequency devices, not too close to the external connector.
3, pay attention to the impedance matching of high-speed signals, the alignment layer and its return current path (return current path), in order to reduce the reflection and radiation of high frequency.
4、Place sufficient and appropriate decoupling capacitors on the power supply pins of each device to moderate the noise on the power supply and ground layers. Pay particular attention to the frequency response and temperature characteristics of the capacitors to ensure that they meet the design requirements.
5、The ground near the external connector can be properly divided from the ground layer and the connector ground can be connected to the chassis ground nearby.
6、Appropriate ground guard/shunt traces can be used next to some particularly high speed signals. But pay attention to the guard/shunttraces on the impact of the characteristic impedance of the alignment.
7, the power layer than the ground layer inside the 20H, H is the distance between the power layer and the ground layer.
26, when a PCB board has more than one digital / analogue function block, the conventional practice is to separate the digital / analogue ground, what is the reason?
The reason for separating the digital/analogue ground is that digital circuits generate noise in the power supply and ground when switching between high and low potentials, the size of the noise is related to the speed of the signal and the size of the current. If the ground plane is not split and the noise generated by the circuits in the digital area is high and the circuits in the analogue area are very close together, the analogue signal will still be interfered with by ground noise even if the digital and analogue signals do not cross. This means that the digital-analogue ground plane can only be used when the analogue circuit area is far away from the digital circuit area where the noise is generated.
27, another approach is to ensure that the digital / analogue layout is separate, and the digital / analogue signal alignment does not cross each other, the entire PCB ground is not divided, digital / analogue ground are connected to this ground plane. What is the rationale?
Digital and analogue signal lines can not cross the requirements because the speed of the digital signal its return current path (return currentpath) will try to flow back to the source of the digital signal along the bottom of the line near the ground, if the digital and analogue signal lines cross, the return current generated by the noise will appear in the analogue circuit area.
28, in the high-speed PCB design schematic design, how to consider the impedance matching problem?
In the design of high-speed PCB circuit, impedance matching is one of the design elements. The impedance value has an absolute relationship with the alignment method, such as whether it is on the surface (microstrip) or the inner layer (stripline/double stripline), the distance to the reference layer (power or ground layer), the width of the alignment, PCB material, etc. will affect the characteristic impedance value of the alignment. This means that the impedance value can only be determined after the wiring has been run. The general simulation software will be due to the line model or the limitations of the mathematical algorithms used and can not take into account some impedance discontinuity in the wiring situation, then the schematic can only be reserved for some terminators (terminations), such as series resistors, to moderate the effect of the impedance discontinuity. The real fundamental solution is to avoid impedance discontinuities when wiring.
29. Where can I find an accurate library of IBIS models?
The accuracy of the IBIS model has a direct impact on the results of the simulation. Basically, IBIS can be regarded as the electrical characteristics of the actual chip I/O buffer equivalent circuit, which can be obtained by converting the SPICE model (measurement can also be used, but it is more limited), and the SPICE information is absolutely related to the chip manufacturing, so the SPICE information of the same device is different from one chip manufacturer to another, and the information in the converted IBIS model will also be different. The data in the converted IBIS model will also vary. This means that if a device from vendor A is used, only they will be able to provide accurate model information for their device, as no one else will know better than them what process their device is made from. If the IBIS provided by the vendor is inaccurate, only the vendor can continue to ask for improvements is the fundamental solution.
30, in the high-speed PCB design, the designer should be considered from those aspects of EMC, EMI rules?
General EMI/EMC design needs to consider both radiated (radiated) and conducted (conducted) two aspects. The former is the higher frequency part (>30MHz) and the latter is the lower frequency part (<30MHz). Therefore, it is important not to focus on the high frequencies and ignore the low frequencies.
A good EMI/EMC design must take into account the placement of devices, the arrangement of PCB layers, the alignment of important interconnects, the choice of devices, etc. If these are not arranged well in advance, the solution afterwards will be half the effort and increase the cost. For example, the clock generator should be located as close as possible to the external connector, the high speed signal should be placed on the inner layer and the impedance should be matched to the reference layer to reduce reflections, the slope of the signal pushed by the device should be as small as possible to reduce the high frequency component, and the decoupling/bypass capacitor should be chosen with the frequency response in mind to reduce The decoupling/bypass capacitors should be selected to ensure that the frequency response is appropriate to reduce power layer noise. In addition, attention is paid to the return path of the high frequency signal current so that the loop area is as small as possible (i.e. the loop impedance loopimpedance is as small as possible) to reduce radiation. It is also possible to control the range of high frequency noise by dividing the ground layer. Finally, the ground point between the PCB and the housing (chassis ground) should be selected appropriately.
31、How to choose an EDA tool?
The current pcb design software, thermal analysis is not a strong point, so it is not recommended, other functions 1.3.4 can choose PADS or Cadence performance to price ratio are good. PLD design for beginners can use the PLD chip manufacturers to provide an integrated environment, in order to do more than a million gates of design can be used to single-point tools.
32. Please recommend an EDA software that is suitable for high-speed signal processing and transmission.
For conventional circuit design, INNOVEDA's PADS is very good, and there is simulation software to work with, and this type of design often accounts for 70% of applications. In doing high-speed circuit design, analogue and digital hybrid circuits, using Cadence's solution should belong to the better performance and price of the software, of course, Mentor's performance is still very good, especially its design process management should be the most excellent.
33、Explanation of the meaning of each layer of the PCB board
topoverlay ---- top layer device name, also called top silkscreen or top component legend, such as R1 C5,IC10. bottomoverlay ---- the same as multilayer ----- if you design a 4-layer board, you place a free pad or via, define it as multilay then its pad will automatically appear on the 4 layers, if you only define it as top layer, then its pad will only appear on the top layer.
34, more than 2G high frequency PCB design, alignment, layout, should focus on what aspects?
More than 2G high frequency PCB belongs to the RF circuit design, not in the scope of high-speed digital circuit design discussion. RF circuit layout (layout) and wiring (routing) should be considered together with the schematic, because the layout and wiring will cause distribution effects. The Mentor boardstation has a dedicated RF design module that can meet these requirements. Moreover, general RF design requires special RF circuit analysis tools, the industry's most famous is agilent's eesoft, and Mentor's tools have a good interface.
35, more than 2G high frequency PCB design, microstrip design should follow which rules?
RF microstrip line design requires a 3D field analysis tool to extract the transmission line parameters. All the rules should be specified in this field extraction tool.
36, For a fully digital signal PCB, there is an 80MHz clock source on the board. In addition to the use of a silk screen (ground), what other circuitry should be used for protection to ensure adequate drive capability?
Ensuring the driving capability of the clock should not be achieved by protection, which is generally achieved by using a clock driver chip. The general concern about clock drive capability is caused by multiple clock loads. A clock driver chip is used to turn one clock signal into several, using a point-to-point connection. Select the driver chip, in addition to ensuring that the basic match with the load, the signal along to meet the requirements (generally clock for along the effective signal), in the calculation of the system timing, to count the clock in the driver chip time delay.
37, if a separate clock signal board, what kind of interface is generally used to ensure that the transmission of the clock signal is affected by the small?
The shorter the clock signal, the smaller the transmission line effect. Using a separate clock signal board will increase the length of the signal wiring. Also the grounding and power supply of the single board is an issue. For long distance transmission, a differential signal is recommended. an LVDS signal can meet the drive capability requirements, but your clock is not too fast for this to be necessary.
38, 27M, SDRAM clock lines (80M-90M), the second and third harmonics of these clock lines are just in the VHF band and interfere a lot with the high frequencies coming in from the receiver side. Apart from shortening the line length, what else can I do?
If the third harmonic is large and the second harmonic is small, this may be because the signal duty cycle is 50%, since in this case there are no even harmonics. In this case the signal duty cycle needs to be modified. In addition, for clock signals that are unidirectional, series matching at the source is generally used. This suppresses secondary reflections, but does not
affect the clock edge rate. The source matching value can be obtained using the formula below.
39、What is the topology of the alignment?
Topology, also known as routing order, is the order in which multiple ports are connected to the network.
40、How can I adjust the topology of the alignment to improve signal integrity?
The signal direction of this network is complex, because the topology affects unidirectional and bidirectional signals, and different level types of signals, so it is difficult to say which topology is beneficial to signal quality. It is difficult to say which topology is beneficial to the signal quality. It is also very demanding for the engineer to understand the circuit principle, the type of signal and even the difficulty of wiring before making a simulation.