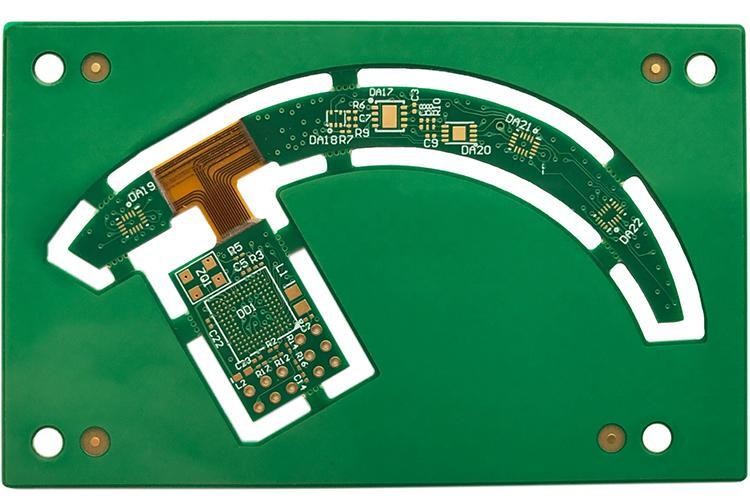
Description
Number of layers: 4 (RIGID), 2 (FLEX)
Board thickness: 1.2mm
Copper thickness: 1oz
Solder Mask: YES, Green, on both sides
Silk Screen: YES, on both sides
Board Finish:ENIG
The temperature and pressure for seamless lamination of rigid-flex boards depend on the specific materials and processes. Generally speaking, the lamination temperature is between 180°C and 220°C, and the pressure is between 25kg/cm² and 35kg/cm². However, these parameters may vary depending on the manufacturer, equipment, and materials.
In actual production, in order to ensure the quality of lamination, manufacturers usually conduct tests and adjustments according to specific circumstances to find the best lamination temperature and pressure. At the same time, factors such as lamination time and buffer materials need to be considered to ensure the performance and reliability of rigid-flex boards.
In the lamination process, the following measures can be taken to control the warpage and deformation of the rigid-flex PCB:
1. Material selection: Choose materials with similar coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) to reduce the dimensional differences when the temperature changes.
2. Control of temperature and pressure: According to the characteristics of the materials and process requirements, accurately control the temperature and pressure during the lamination process. Ensure uniform temperature distribution and avoid excessive or too low pressure.
3. Preheating and pre-pressing: Before formal lamination, preheat and pre-press the flexible board and the hard board, which helps to reduce the stress differences between the materials.
4. Lamination sequence: Adopt an appropriate lamination sequence, such as gradually applying pressure from the center to the edges to ensure uniform pressure distribution.
5. Control of humidity: Keep an appropriate humidity environment to avoid the materials from absorbing moisture or being too dry, which helps to reduce the risk of warpage and deformation.
6. Optimization of the laminated structure: Reasonably design the laminated structure of the rigid-flex PCB to avoid asymmetric or overly complex layouts to reduce stress concentration.
7. Use of buffering materials: During the lamination process, appropriate buffering materials can be used to reduce the impact of pressure on the flexible board and reduce the possibility of warpage and deformation.
8. Process monitoring and adjustment: Monitor the temperature, pressure and the shape of the board in real time during the lamination process, and make timely adjustments as needed to ensure the lamination quality.
9. Post-treatment: After lamination, appropriate post-treatment such as baking or cooling can be carried out to stabilize the performance and shape of the board.
It should be noted that different materials and processes may require different control methods. Therefore, in actual production, experiments and optimizations need to be carried out according to the specific situation to find the most suitable method to control the warpage and deformation of the rigid-flex PCB. At the same time, strict process control and quality inspection are also the keys to ensuring product quality.