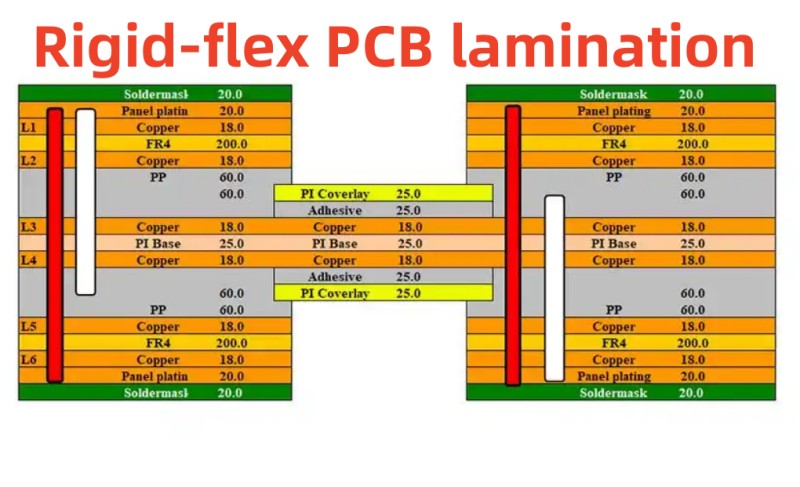
Rigid-flex boards lamination related
Rigid-flex boards lamination related
The lamination of rigid-flex boards is a key process, which mainly includes the following steps:
Preparation
- Material preparation: prepare rigid circuit boards, flexible circuit boards, prepregs (PP sheets), covering films and other materials. Rigid boards and flexible boards need to be pre-processed to ensure that the surface is clean and free of impurities.
- Equipment debugging: debug the lamination equipment, such as the hot press, and set the lamination temperature, pressure and time and other parameters. Different materials and board types have different parameters.
Stacking design
- According to the design requirements, stack the flexible board, prepreg, rigid board, etc. Generally, the prepreg is placed on the rigid board first, and then the flexible board is placed on the prepreg, and then other auxiliary materials such as covering films are covered as needed. Pay attention to alignment when stacking to avoid offset.
Lamination process
- Pre-pressing: Put the stacked board into the hot press, apply a small pressure first, so that the layers of materials are initially fitted and the air is removed. The pre-pressing temperature is usually in a lower range, such as 80-100℃, and the pressure is determined according to the size and material of the board, generally 0.5-1MPa, and the pre-pressing time is about 5-10 minutes.
- Hot pressing: After the pre-pressing is completed, the temperature and pressure are increased for hot pressing. The hot pressing temperature is generally 150-200℃, the pressure is increased to 1-3MPa, and the duration is about 30-60 minutes depending on the thickness of the board and the material properties. During this process, the prepreg melts and fills the gap, so that the rigid board and the flexible board are firmly combined.
- Cooling: After the hot pressing is completed, stop heating and let the pressed board cool naturally in the press or use forced cooling to cool to room temperature. During the cooling process, the material solidifies and forms a stable bonding structure.
Quality inspection
- After the pressing is completed, the appearance of the soft-rigid combination board is inspected to check for defects such as bubbles, delamination, and lack of glue. The conductivity and insulation performance of the circuit will also be tested by electrical testing and other means to ensure that the pressing quality meets the requirements.
The following aspects should be considered when selecting materials for lamination of rigid-flex boards:
Rigid board materials
- Mechanical properties: According to the product's requirements for strength and stability, select suitable rigid board materials, such as FR-4 (glass fiber epoxy resin), which has high strength and good insulation properties and is suitable for general electronic equipment; if higher strength and heat resistance are required, ceramic-based composite materials can be selected.
- Electrical properties: Consider the material's electrical parameters such as dielectric constant and dielectric loss to meet the circuit's signal transmission requirements. For example, for high-frequency circuits, materials with low and stable dielectric constants should be selected to reduce signal distortion and transmission delay.
Flexible board materials
- Flexibility and bending resistance: According to the product's usage scenarios and bending requirements, select flexible board materials with appropriate flexibility and bending resistance. For example, polyimide (PI) film has excellent bending resistance and high strength, and is suitable for areas that require frequent bending; polyester (PET) film has low cost and good flexibility, and can be used in some occasions where bending resistance is not required.
- Insulation performance and thickness: The insulation performance of the flexible board material should be good to prevent short circuits. At the same time, according to the space limitations and performance requirements of the product, select the flexible board material of appropriate thickness, which is generally between 0.05-0.15mm.

Adhesive material
- Adhesive strength: The adhesive strength of the adhesive material (such as prepreg) should be sufficient to firmly bond the rigid board and the flexible board to withstand various stresses during the use of the product.
- Fluidity and filling: During the lamination process, the adhesive material should have good fluidity and filling, and be able to fully fill the gap between the rigid board and the flexible board, exclude air, and form a tight bonding interface.
Covering material
- Insulation protection performance: Covering materials such as covering films should have good insulation performance, which can effectively protect the circuit from the influence of the external environment and prevent problems such as short circuits and leakage.
- Chemical resistance and wear resistance: Considering the use environment of the product, select covering materials with good chemical resistance and wear resistance to ensure the stability and reliability of the rigid-flexible board during long-term use.
When laminating rigid-flex boards, the following methods can be used to ensure the alignment accuracy of each layer of material:
Design and manufacture high-precision positioning systems for laminating rigid-flex boards
- Use positioning holes: Design positioning holes on rigid boards and flexible boards, usually located at the edge or specific position of the board. Before lamination, insert the positioning pins into the positioning holes to accurately fix each layer of material in the preset position, which can effectively limit the movement of the material during the lamination process.
- Use optical positioning system: Some advanced lamination equipment is equipped with an optical positioning system, which uses a camera to shoot the marking points on each layer of material, and accurately adjusts the position of the material through computer image processing technology to achieve high-precision alignment.
Optimize material processing and processing technology for laminating rigid-flex boards
- Laminating rigid-flex boards material cutting accuracy control: When cutting rigid boards, flexible boards, prepregs and other materials, use high-precision cutting equipment and processes to ensure that the material edges are neat and the size accuracy is high, reducing the alignment difficulties caused by material size deviations.
- Laminating rigid-flex boards surface treatment uniformity: Each layer of material is surface treated before lamination, such as cleaning and roughening, to ensure uniform surface conditions. This allows the material to be evenly stressed during the lamination process, avoiding local displacement caused by differences in surface properties, and is conducive to maintaining alignment accuracy.
Strict production process control and testing for laminating rigid-flex boards
- Employee training and operating specifications: Operators must undergo professional training and be familiar with the lamination process and operating requirements. During the lamination and lamination operations, strictly follow the operating specifications to ensure that each layer of material is placed accurately and the operation is gentle to avoid material displacement caused by human factors.
- Online detection and adjustment: During the lamination process, online detection technology is used, such as installing sensors in the lamination equipment to monitor the position status of each layer of material in real time. Once alignment deviation is found, timely adjustments are made to ensure lamination quality.
During the lamination of rigid-flex boards, the following aspects should be noted:
The lamination of rigid-flex boards temperature control
- The lamination temperature needs to be precisely set and controlled according to the material characteristics. If the temperature is too high, the material may be over-cured, brittle, or even damage the circuit; if the temperature is too low, the material will not be fully cured, resulting in insufficient bonding strength.
- During the heating process, a suitable heating rate should be adopted to avoid thermal stress caused by rapid temperature changes, which will affect the performance of the board and the bonding quality between the layers.

the lamination of rigid-flex boards pressure control
- The applied pressure should be uniform and moderate. If the pressure is too low, the layers of materials cannot fit tightly, and defects such as delamination and bubbles are prone to occur; if the pressure is too high, the flexible board may be deformed, the rigid board may be broken, or the circuit structure may be damaged.
- During the lamination process, the pressure should be reasonably adjusted according to factors such as the thickness of the board and the type of material to ensure uniform pressure distribution on the entire board surface and ensure good bonding of the layers of materials.
The lamination of rigid-flex boards time control
- The lamination time is interrelated with temperature and pressure and needs to be considered comprehensively. If the time is too short, the curing reaction of the material is not sufficient, which affects the bonding force and the performance of the board; if the time is too long, it will not only reduce production efficiency, but also may have an adverse effect on the material performance.
- For different types and specifications of rigid-flex boards, the optimal lamination time should be determined through experiments and strictly controlled during the production process.
The lamination of rigid-flex boards environmental control
- The cleanliness of the lamination environment is crucial. The working area should be kept clean and dust-free to prevent dust, impurities, etc. from mixing into the laminated materials and affecting the electrical performance and appearance quality of the board.
- At the same time, the humidity of the environment will also affect the material. Excessive humidity may cause the material to absorb moisture, produce bubbles during the lamination process, or reduce the insulation performance of the material. Therefore, the environmental humidity needs to be controlled within an appropriate range.
The lamination of rigid-flex boards material placement and fixation
- When stacking each layer of material, ensure accurate positioning and high alignment accuracy to prevent offset. The positioning holes, positioning pins or optical positioning systems mentioned above can be used to assist positioning.
- After placing the material, it should be properly fixed to avoid material movement due to pressure and temperature changes during the lamination process, which will affect the lamination quality.
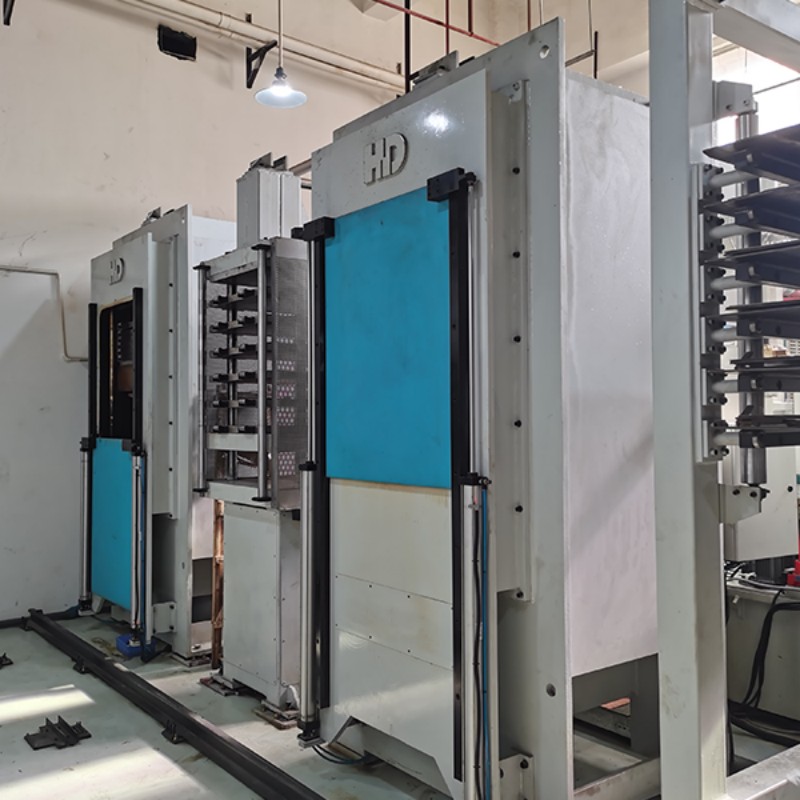
When laminating rigid-flex board, the press needs to ensure the following performance to ensure the lamination quality:
- Accurate temperature control: The press should have an accurate temperature control system when laminate rigid-flex boards, and the temperature control accuracy should usually be within ±2℃ to ensure that the temperature is uniform and stable during the lamination process to meet the curing requirements of different materials. At the same time, the heating rate must also be controllable, generally within the range of 2-5℃ per minute, to avoid adverse effects of rapid temperature changes on the material.
- Uniform pressure distribution: The pressure system of the press must be able to ensure uniform pressure distribution on the entire lamination surface when laminate rigid-flex boards, and the pressure deviation does not exceed ±5%. This requires the press plate to have good flatness and rigidity, and the pressure application mechanism to be accurately adjusted to avoid problems such as poor material bonding and local deformation caused by uneven pressure.
- Stable pressure output: During the lamination process, the press needs to provide stable pressure output, and the pressure fluctuation should be controlled within ±0.1MPa. Stable pressure helps to fully fit and cure the materials, and prevents defects such as interlayer gaps or bubbles caused by pressure fluctuations.
- High-precision positioning system: The press machine needs to be equipped with a high-precision positioning system with a positioning accuracy of ±0.05mm. Through positioning pins, optical recognition and other methods, ensure that the layers of materials of the soft and hard combination board are accurately aligned during the lamination process to avoid offset.
- Good vacuum performance: With a good vacuum system when laminate rigid-flex boards, the air in the chamber can be quickly extracted before lamination, so that the vacuum degree reaches the range of 10-100Pa, the air between the materials is removed, the bubble generation is reduced, and the lamination quality is improved.
- Reliable mechanical structure: The mechanical structure of the press machine should have sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand the high pressure during the lamination process without deformation, ensure the stability and repeatability of the lamination process, and ensure the consistent quality of each lamination.
To prevent the occurrence of delamination of rigid-flexible boards during lamination, the following measures can be taken:
Material aspect
- Optimize material selection: Select semi-cured sheets with good bonding performance, which can be well bonded with rigid and flexible board materials during lamination. At the same time, ensure that the surface cleanliness and roughness of rigid and flexible board materials are appropriate to facilitate bonding.
- Material pretreatment: Surface treatment of rigid and flexible boards, such as cleaning, degreasing, and roughening, is performed to improve surface energy and enhance bonding with bonding materials.
Process aspect
- Control rigid-flex PCB lamination parameters: Accurately control the temperature, pressure, and time of lamination according to material properties and board structure. The heating rate should not be too fast, generally controlled at 2-5℃ per minute to avoid delamination due to excessive thermal stress. The pressure should be uniform and moderate, and the pressure deviation on the entire lamination surface should not exceed ±5%, so that each layer of material is fully bonded. The lamination time should be sufficient to ensure that the bonding material is fully cured, but it should not be too long to prevent the material from aging and becoming brittle and affecting the bonding strength.
- Use appropriate rigid-flex PCB lamination methods: For example, if a step-by-step lamination process is used, pre-press at a lower pressure first to position and fit each layer of material, remove some air, and then gradually increase the pressure to the final lamination pressure, which can effectively reduce the delamination phenomenon.
Equipment
- Maintain equipment accuracy: The press plate of the press should have good flatness and rigidity, and the flatness error should not exceed ±0.05mm to ensure uniform pressure distribution. At the same time, the positioning system should be accurate to ensure that each layer of material is accurately aligned during the lamination process, and the positioning accuracy should be within ±0.05mm to prevent local stress concentration and delamination due to position deviation.
- Regularly maintain equipment: Regularly maintain and calibrate the heating, pressure and vacuum systems of the press to ensure stable and reliable performance. For example, the vacuum system should be able to achieve a vacuum degree of 10-100Pa in the lamination chamber to effectively remove air and avoid bubbles causing delamination.
The following are some advanced equipment and technologies that can improve the quality of rigid-flex board lamination:
Advanced equipment
- High-precision press: Equipped with precise temperature and pressure control systems and high-flatness press plates, such as presses using hot oil circulation heating, the temperature uniformity can reach ±1°C, and the pressure control accuracy can reach ±0.05MPa, which can ensure the stability and consistency of various parameters during the lamination process.
- Automatic positioning system equipment: Using optical recognition technology, the camera captures the positioning marks on the board and automatically adjusts the position of each layer of material. The positioning accuracy can be as high as ±0.02mm, which effectively improves the alignment accuracy of each layer and reduces the deviation caused by human factors.
- Vacuum lamination equipment: Equipped with a high-performance vacuum system, the vacuum degree of the lamination chamber can be increased to 5-10Pa in a short time, which can more thoroughly remove air, reduce bubbles and stratification, and lamination in a vacuum environment, which helps to improve the fit of the material.
Advanced technology
Laser positioning technology for rigid-flex PCB lamitation:
- Before lamination, laser is used to mark the positioning of each layer of material, and then the laser tracking system is used to monitor and adjust the material position in real time during the lamination process to achieve high-precision inter-layer alignment, and the positioning accuracy can be controlled within ±0.01mm.
Intelligent lamination technology:
- With the help of sensors, the temperature, pressure, displacement and other parameters in the lamination process are monitored in real time, and the data is analyzed and processed by computer algorithms to automatically adjust the lamination parameters to achieve intelligent control of the lamination process and improve the stability and consistency of the lamination quality.
Plasma treatment technology for rigid-flex board lamination:
-Plasma treatment of the material surface before lamination can remove surface pollutants and oxides, increase surface roughness and activity, improve the adhesion between materials, effectively prevent stratification, and improve lamination quality.
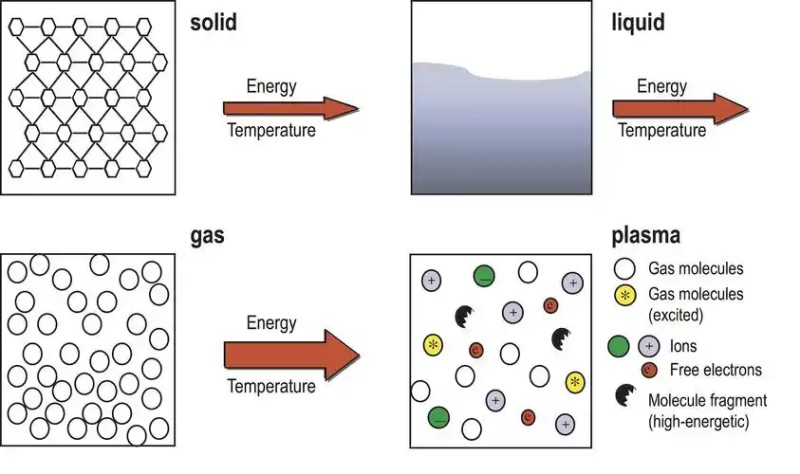
Plasma treatment technology generally has the following specific operating steps for treating hard-flex board materials:
Preparation before treatment
- Check equipment: Ensure that the plasma treatment equipment for rigid-flex board lamination is operating normally, including the vacuum pump, plasma generator, gas supply system and other components are fault-free, and the vacuum chamber is well sealed.
- Prepare materials: Clean the hard-flex board materials to be treated, remove dust, oil and other impurities on the surface, and then put them on the sample table in the vacuum chamber. Pay attention to placing them neatly to avoid mutual blocking and affecting the treatment effect.
Vacuuming
- Start the vacuum pump: Close the vacuum chamber door, start the vacuum pump, and extract the air in the chamber to achieve a certain vacuum degree in the chamber, generally in the range of 10-100Pa.
Introduce gas
- Select gas: According to the characteristics of the material and the processing requirements, select a suitable plasma gas, such as oxygen, nitrogen, argon, etc. Usually, oxygen is often used to remove organic impurities, and argon is suitable for improving the roughness of the material surface.
- Gas introduction: Open the gas supply system, and introduce the selected gas into the vacuum chamber according to the set flow rate and pressure, so that the gas pressure in the chamber is stabilized at a certain value, generally 100-1000Pa.
Generate plasma
- Start the plasma generator: Adjust the power, frequency and other parameters of the plasma generator to generate stable plasma. The power is generally between 100-1000W, and the frequency is 13.56MHz or higher. The plasma is accelerated under the action of the electric field and reacts physically and chemically with the surface of the material of rigid-flex board.
- Processing time control: Determine the appropriate processing time according to the type, thickness and processing requirements of the material, generally 1-15 minutes. If the processing time is too short, the expected processing effect may not be achieved; if the processing time is too long, it may cause excessive damage to the surface of the material.
Post-processing
- Stop plasma generation: After the rigid-flex board lamination processing time is over, turn off the plasma generator and stop the generation of plasma.
- Exhaust gas: Turn off the gas supply system, open the exhaust valve, and exhaust the gas in the chamber.
- Remove the material: After the pressure in the chamber returns to normal pressure, open the chamber door and remove the processed rigid-flex board material. At this time, the surface of the material has high activity and roughness, so you should avoid touching it directly with your hands to prevent re-contamination.
During the entire operation process, the operator must strictly follow the operating procedures of the equipment to ensure the safety and stability of the treatment process. At the same time, the treatment parameters should be optimized and adjusted according to the actual situation to obtain the best treatment effect.
When using plasma processing technology to process rigid-flex board materials, the following aspects need to be noted:
Parameter setting
- Power selection: Too high power may cause excessive etching of the rigid-flex material surface, affecting performance; too low power will result in poor processing effect. The optimal power range should be determined through experiments based on factors such as material type and thickness.
- Processing time control: Too long a time for rigid-flex lamination will cause changes in the surface properties of the material, such as brittleness and yellowing; too short a time will not achieve the expected processing effect. The time needs to be precisely controlled according to the material properties and the purpose of the treatment.
- Gas type and flow rate: Different gases have different chemical properties and different effects on the rigid-flex PCB material. Choose the appropriate gas according to the processing requirements of the material surface, and accurately control the gas flow rate. Too large or too small a flow rate will affect the generation of plasma and the processing effect.
Material aspect
- Material compatibility: Different rigid-flex board materials may react differently to plasma treatment. Some materials may be sensitive to specific gases or processing conditions. It is necessary to understand the material properties before processing to avoid material performance degradation due to processing.
- Material cleanliness: Impurities on the surface of the rigid-flex PCB material before treatment will affect the interaction between plasma and the material and reduce the treatment effect. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the surface of the material is clean and free of pollutants such as oil and dust.
Equipment
- Equipment maintenance: Regularly maintain and calibrate the plasma treatment equipment to ensure the normal operation of the equipment's vacuum pump, plasma generator and other components to ensure the stability and repeatability of the treatment process.
- Vacuum control: Vacuum is an important factor affecting the effect of plasma treatment for rigid-flex board lamination. The vacuum of the vacuum chamber must be controlled within an appropriate range. Too high or too low vacuum will affect the generation and properties of plasma.
Safety
- Personnel protection: Harmful substances such as ultraviolet rays and ozone may be generated during plasma treatment. Operators must wear protective glasses, masks and other protective equipment to prevent injury.
- Gas safety: Some of the gases used, such as oxygen and argon, are flammable or asphyxiating. It is necessary to ensure the safety of gas storage and use to prevent leakage.