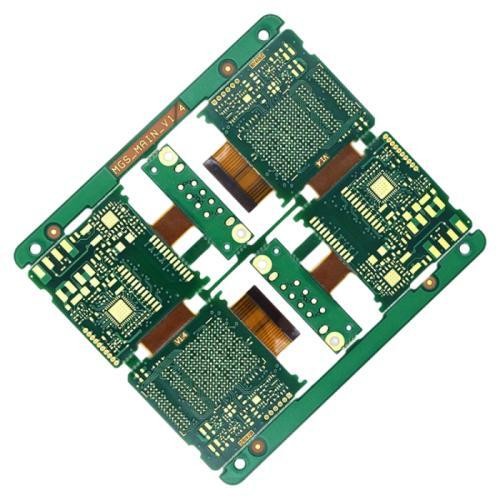
Description
Number of layers: 4 (RIGID), 2 (FLEX)
Size: 136.1 x 100.5mm
Board thickness: 1.8mm
Copper thickness: 1oz
Solder Mask: YES, Green, on both sides
Silk Screen: YES, on both sides
Board Finish:ENIG
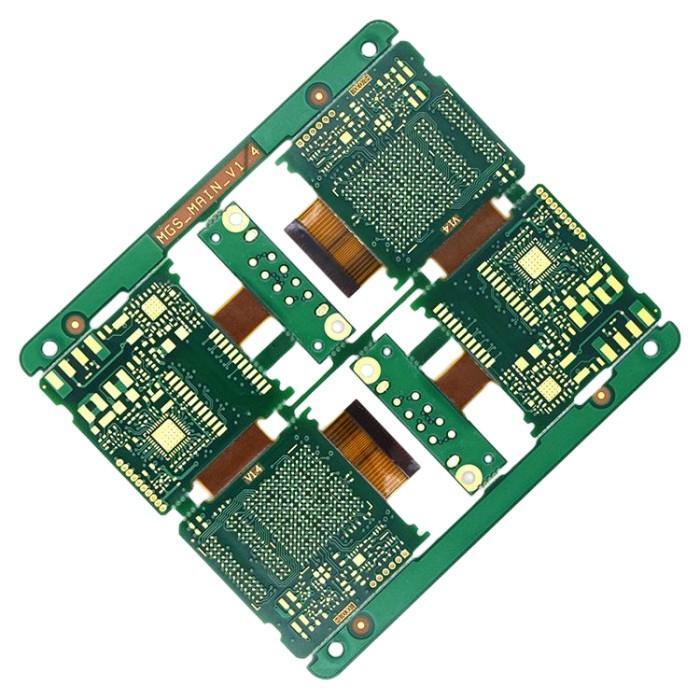
Rigid-flex PCB is a kind of circuit board that combines flexible circuit board (FPC) and rigid circuit board (PCB) through processes such as lamination. It has both the flexibility of FPC and the rigidity of PCB, and has the advantages of high-density connection, high-speed transmission, good flexibility and high stability.
The production process of rigid-flex PCB is relatively complex and requires both FPC production equipment and PCB production equipment. Firstly, the circuit and shape of the flexible combined board are designed by electronic engineers, and then processed and planned by CAM engineers to arrange the FPC production line and PCB production line to produce the required FPC and PCB respectively. Finally, the FPC and PCB are seamlessly laminated through the laminating machine, and a series of detailed treatments are carried out to make the rigid-flex PCB.
How to Choose Flexible Printed Circuit Boards and Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Boards?
When choosing between flexible printed circuit boards (FPC) and rigid-flex printed circuit boards, several key factors need to be considered:
1. Rigid-flex PCB and FPC application requirements: Clearly define the specific use and functional requirements of the product. If flexible connections and bending within a limited space are required, FPC might be more suitable. If both flexibility and certain rigid support areas are needed, such as fixed structural strength in specific parts, then rigid-flex printed circuit boards might be a better choice.
2. The performance requirements of Rigid-flex PCB and FPC : Consider electrical performance, signal transmission quality, impedance control, etc. Different boards may perform differently in these aspects. The decision should be based on the specific circuit design and signal requirements.
3. Rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB space limitations: Evaluate the size and shape of the installation space. FPC can adapt to more compact and complex spaces. While rigid-flex printed circuit boards also have their advantages in space utilization, they might not be as flexible as FPC.
4. The reliablility of Rigid-flex PCB and FPC : There may be certain reliability risks at the connection points of rigid-flex printed circuit boards. The stability and durability in the usage environment need to be evaluated. For FPC, the bending fatigue life and other reliability indicators should be concerned.
5. Rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB Cost budget: Generally speaking, the cost of rigid-flex printed circuit boards is relatively high. If cost is an important limiting factor, FPC might be a more economical choice, but the performance and reliability should also be comprehensively considered to meet the requirements.
6. manufacturing process and complexity of Rigid-flex PCB and FPC : Understand the manufacturer's capabilities and process level. Complex designs may pose higher requirements on the manufacturing process, affecting cost and delivery time.
7. Rigid-flex PCB and FPC heat dissipation requirements: If the equipment has high heat dissipation requirements, it is necessary to evaluate the heat dissipation performance of FPC and rigid-flex printed circuit boards and choose a solution that can effectively dissipate heat.
Comprehensively considering the above factors can help you make a more appropriate choice.
The Similarities and Differences Between Flexible Printed Circuit Boards and Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Boards
The similarities and differences between flexible printed circuit boards (FPC) and rigid-flex printed circuit boards are as follows:
Similarities:
1. Both belong to the category of printed circuit boards (PCB) and are used to achieve electrical connections between electronic components.
2. Both rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB adopt similar manufacturing processes and materials, such as substrate materials, cover layer materials, conductive layers, etc.
3. Both rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB can adapt to the needs of miniaturization, lightweight, and high-density wiring to a certain extent.
Differences:
1. Structure: FPC is completely flexible and can be freely bent, folded, and twisted; rigid-flex printed circuit boards are composed of rigid and flexible parts.
2. Mechanical strength: FPC is overall softer and has relatively lower mechanical strength; the rigid part of rigid-flex printed circuit boards provides higher mechanical strength and support.
3. Application scenarios: FPC is often used in devices that require frequent bending or have limited space, such as internal connections in mobile phones and tablet computers; rigid-flex printed circuit boards are suitable for occasions where both bending requirements and some areas require rigid support, such as aerospace and medical equipment.
4. Cost: Generally speaking, the manufacturing cost of rigid-flex printed circuit boards is usually higher than that of FPC.
5. Design complexity: The design of rigid-flex printed circuit boards is more complex than that of FPC, and the transition and connection between the rigid and flexible areas need to be considered.
6. Heat dissipation performance: The rigid part of rigid-flex printed circuit boards is relatively more conducive to heat dissipation, while the heat dissipation performance of FPC is relatively poor.
7. Maintenance difficulty: The maintenance of FPC is relatively simple, while the maintenance of rigid-flex printed circuit boards is more difficult due to its complex structure.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards and Rigid-Flex Printed Circuit Boards in Performance
The performance advantages and disadvantages of FPC:
Advantages:
1. Flexible PCB has good flexibility: It can withstand multiple bends, folds, and twists, suitable for applications that require dynamic movement or limited space.
2. Flexible PCB light and thin: Helps to reduce the weight and thickness of the device, meeting the demand for thin and light modern electronic products.
3. Flexible PCB good signal transmission performance: Performs well in high-frequency signal transmission, and the signal integrity is good.
4. High customizability: Can be custom-designed according to specific shapes and sizes.
Disadvantages:
1. Flexible PCB is low mechanical strength: Easily damaged by external forces without external support.
2. Flexible PCB is relatively poor heat dissipation performance: Due to its structural characteristics, heat dissipation is not as efficient as that of rigid boards.
3. High cost: Especially for complex multilayer FPC.
The performance advantages and disadvantages of rigid-flex printed circuit boards:
Rigid-flex PCB advantages:
1. Rigid-flex PCB combine the characteristics of rigidity and flexibility: Provides flexibility in the parts that need to be bent and rigidity in the parts that need support, having better adaptability.
2. Improves space utilization: Can achieve a compact layout in complex spaces.
3. Rigid-flex has good electrical performance: Can achieve high-density wiring and precise impedance control.
4. Enhances reliability: The rigid part provides better protection and support for key components.
Disadvantages:
1. Rigid-flex PCB has complex design and manufacturing: The transition between the rigid and flexible areas needs to be considered, increasing the design difficulty and complexity of the manufacturing process.
2. The high cost of Rigid-flex PCB: Due to its complex structure and manufacturing process, the cost is usually higher than that of pure rigid or flexible boards.
3. Rigid-flex PCB is difficult maintenance: Once a fault occurs, the maintenance is difficult.
4. The heat dissipation performance of Rigid-flex PCB is still limited: Although the rigid part helps with heat dissipation, the overall heat dissipation performance may not be as good as that of all-rigid boards.
Rigid-flex PCB is widely used in the fields of computers, communications, consumer electronics, automobiles, etc., such as portable digital products such as mobile phones, digital cameras, digital video cameras, and automotive electronic devices such as automotive sensors and driving recorders. In these applications, the rigid-flex PCB can save the internal space of the product, reduce the volume of the finished product, and improve the performance of the product.