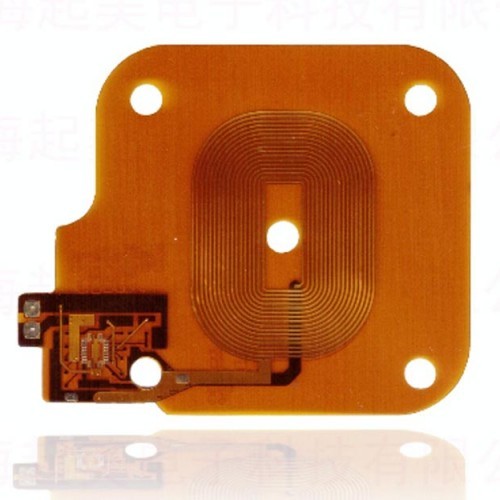
Description
Flexible PCB manufacturers typically produce flexible PCBs in the following steps:
1. Flexible PCB manufacturers design and planning: Based on customer requirements and circuit designs, the layout and structure of the flexible PCB are determined.
2. Flexible PCB manufacturers prepare of material: Purchase the required substrate materials (such as polyimide films), cover layer materials, conductive materials (usually copper foils), as well as various chemical solutions and auxiliary materials.
Polyimide films are commonly used as the substrate material in flexible printed circuit boards (FPCs), also known as flex boards. Here is a detailed introduction to polyimide films in this context:
Properties:
- High Temperature Resistance: FPC Polyimide films can withstand high temperatures without significant degradation in their properties. This makes them suitable for applications where the circuit may be exposed to elevated temperatures during operation or processing.
- Chemical Resistance: They have excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, acids, and bases. This chemical stability helps ensure the longevity and reliability of the flex board in various environments.
- Flexibility and Ductility: Polyimide films offer good flexibility and can be bent, folded, and twisted without cracking or losing their electrical properties. This flexibility is crucial for applications where the circuit needs to conform to complex shapes or undergo repeated movement.
- Electrical Insulation: They provide excellent electrical insulation, preventing electrical shorts and ensuring the proper functioning of the circuits.
- Low Dielectric Constant: This property is important for high-frequency applications as it reduces signal loss and enhances signal transmission.
Polyimide films are typically produced through a series of chemical reactions. The process involves the polymerization of monomers to form the polyimide polymer, which is then processed into a film through techniques such as extrusion or casting.
Advantages in flex Board Applications:
- Compact and Lightweight Designs: The flexibility of polyimide films enables the creation of compact and lightweight circuits, which is essential in portable and space-constrained electronic devices.
- Reliability: Their resistance to temperature, chemicals, and mechanical stress contributes to the long-term reliability of the flex board.
- High-Performance Circuits: The low dielectric constant and good electrical insulation properties allow for the design of high-performance circuits, especially in applications requiring high-speed data transmission.
- Cost: Polyimide films can be relatively expensive compared to some other substrate materials, which can increase the overall cost of the flex board.
- Moisture Absorption: They have some moisture absorption tendencies, which may affect their properties over time if not properly protected.
- Pretreat the substrate, including cleaning and surface roughening.
- Transfer the circuit pattern onto the substrate through photolithography processes. This may involve coating photosensitive materials, exposure, development, and etching.
4. Lamination: If it is a multilayer flexible PCB, laminate the inner layers with prepreg materials or bonding sheets to form a multilayer structure.
The lamination structure of a flexible PCB (Flexible Printed Circuit Board) is usually composed of the following main parts:
- Flexible PCB's Cover Layer: Usually made of materials such as polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET), it is used to protect the circuit from environmental influences and mechanical damage.
- Conductive Layer of Flexible PCB: This is the copper foil layer that forms the circuit. The thickness of the copper foil varies depending on the current-carrying requirements and design specifications.
- Adhesive Layer of Flexible PCB: It is used to bond the conductive layer to the substrate or other layers, and is usually a special glue or resin.
- Flexible PCB Substrate: The common substrate material is also polyimide, which provides support and flexibility for the circuit.
Different application scenarios and design requirements can lead to differences in the lamination structure of flexible PCBs, but its basic components usually include the above aspects.
5. Drilling: Flexible PCB manufacturers use a CNC drilling machine to drill holes at the required positions to achieve electrical connections between the layers.
The drilling of flexible PCBs (Flexible Printed Circuit Boards) is an important step in the manufacturing process, but it has some unique challenges and requirements compared to the drilling of rigid PCBs.
During the drilling process of flexible PCBs, the following points need special attention:
- Flexible PCBs Drill bit selection: Special designed drill bits are usually used. The shape and material of the cutting edge should be adapted to the characteristics of the flexible material to reduce damage and delamination of the board.
- Drilling parameters of flexible PCBs: Including rotational speed, feed rate, and cutting depth, etc., which need to be carefully adjusted to ensure the drilling quality and avoid excessive cutting that causes the board to deform or be damaged.
- Flexible PCBs Positioning accuracy: Since flexible PCBs are prone to movement and deformation, the positioning before drilling must be very precise to ensure the accuracy of the hole positions.
- Flexible PCBs Stress reduction: The stress generated during the drilling process may cause the flexible board to curl or deform. Adopting appropriate cooling and lubrication measures can help reduce stress.
- Flexible PCBs Laminate processing: If it is a multilayer flexible PCB, it is necessary to ensure the alignment and fixation between the layers to prevent layer misalignment during drilling.
6. Copper Plating: Flexible PCB manufacturers plate copper inside the drilled holes to form conductive paths.
The copper plating process of flexible PCB usually includes the following steps:
- Flexible PCB manufacturers prepare the copper plating solution: The main components of the copper plating solution are copper sulfate and tartaric acid, and the reaction time and temperature need to be strictly controlled.
- Pre-treatment of the flexible PCB: The purpose of pre-treatment is to clean and activate the copper layer on the surface of the PCB, which is the key to ensuring uniform copper plating on the PCB surface.
- Immerse the flexible PCB in the copper plating solution: The PCB is immersed in the copper plating solution, and copper ions will gradually deposit on the surface of the PCB, thereby forming a uniform copper electrodeposition layer. Control the deposition time and temperature to ensure the thickness and uniformity of the copper layer on the PCB surface.
- Cleaning and post-treatment of Flexible PCB manufacturers: Perform cleaning and post-treatment, including cleaning the PCB, removing areas where the copper layer is not plated, and post-treatment operations to protect the PCB from corrosion.

8. Cover Layer Lamination: Laminate the cover layer material on the surface of the circuit to provide protection and insulation.
9. Surface Treatment: Flexible PCB manufacturers perform surface treatment processes such as gold plating, nickel plating, electroless gold plating, etc., to improve solderability and corrosion resistance.
10. Electrical Performance Testing: Flexible PCB manufacturers use professional testing equipment to conduct electrical performance tests on the flexible PCB to check for issues such as short circuits and open circuits.
11. Outline Processing: Flexible PCB manufacturers according to the design requirements, use CNC milling machines or laser cutting machines to cut and shape the flexible PCB.
12. Final Inspection: Flexible PCB manufacturers conduct a comprehensive appearance inspection, dimensional measurement, and performance test on the finished flexible PCB to ensure it meets quality standards.
13. Packaging and Shipping: Qualified flexible PCBs are packaged and protected by Flexible PCB manufacturers and then delivered to customers.
Throughout the production process, Flexible PCB manufacturers need to strictly control the cleanliness, temperature, and humidity of the production environment to ensure the stability and reliability of product quality. At the same time, continuously optimize the processes and procedures to improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
How to Choose a Reliable Flexible PCB Manufacturer in China?

Here are some suggestions for choosing a reliable flexible PCB manufacturer in China:
1. Research and evaluate the flexible PCB manufacturer reputation: Use the internet search, industry forums, and review websites to learn about the reputation and customer reviews of different manufacturers.
2. Examine the flexible PCB manufacturer production capacity: Inspect the manufacturer's production facilities, the advancement of equipment, and whether they can meet your production volume requirements.
3. Quality certifications: Confirm whether the flexible PCB manufacturer has relevant quality certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates their commitment to quality control.
4. Technical capabilities: Understand flexible PCB manufacturer technical expertise in flexible PCB design and manufacturing, including whether they can handle complex designs and multi-layer structures.
5. Raw material sources: High-quality raw materials are crucial for ensuring product quality. Inquire about flexible PCB manufacturer raw material suppliers and quality control measures.
6. Customization capabilities: If you have specific needs or customization requirements, ensure that the flexible PCB manufacturer has the corresponding capabilities and flexibility to meet these needs.
7. After-sales service: Good after-sales support is essential for resolving potential problems. Understand flexible PCB manufacturer after-sales service policies and response times.
8. Visit the factory: If possible, visit the flexible PCB manufacturer's factory in person to inspect the production process and management situation.
9. Refer to case studies: Request the flexible PCB manufacturer to provide case studies of similar products they have produced for other customers to evaluate their actual achievements.
10. Price reasonableness: Compare the quotations from different flexible PCB manufacturer, but do not only focus on the lowest price option. Consider quality and service comprehensively.
11. Industry experience: Choose a flexible PCB manufacturer with rich industry experience. They are usually better at dealing with various production challenges.
12. Communication and cooperation attitude: Evaluate the flexible PCB manufacturer's cooperation attitude and communication efficiency during the initial communication, which will affect the smooth progress of the project.
By considering the above factors comprehensively, you can select a reliable flexible PCB manufacturer in China.
What are the impacts of the advanced production facilities and equipment of flexible PCB manufacturers on product quality?
The advancement of the production facilities and equipment of flexible PCB manufacturers has the following important influences on product quality:
1. Precision and accuracy: Advanced equipment can achieve higher manufacturing precision and accuracy, ensuring that key parameters such as the circuit layout, hole diameter, and line width of the flexible PCB meet strict design requirements, thereby reducing errors and defects.
2. Consistency and stability: Advanced production facilities contribute to maintaining the consistency and stability of product quality in large-scale production. They can control various parameters in the production process, such as temperature, pressure, and exposure time, more precisely, making the performance and quality of each flexible PCB relatively uniform.
3. flexible PCB manufacturers handle material capabilities: Good equipment can handle various materials required for flexible PCB production, such as substrates, cover layers, and conductive materials, more effectively. This helps improve the adhesion, adhesion, and corrosion resistance of the materials, thereby enhancing the overall quality and reliability of the flexible PCB.
4. Detection and monitoring: Advanced detection equipment of flexible PCB manufacturers can more sensitively detect subtle defects and potential problems in the product, such as short circuits, open circuits, and uneven thickness. Timely monitoring and detection can allow for adjustments and improvements during the production process to avoid the generation of defective products.
5. Adaptation to complex designs: Modern production facilities of flexible PCB manufacturers can handle increasingly complex flexible PCB design requirements, such as multi-layer structures and high-density wiring. This helps manufacturers produce high-quality flexible PCBs that meet the needs of high-end applications.
6. Production efficiency: Advanced equipment of flexible PCB manufacturers often has higher production efficiency, which can shorten the production cycle and reduce production costs. At the same time, an efficient production process also reduces the possibility of the product being affected by the external environment during the manufacturing process, which is conducive to ensuring quality.
In conclusion, the advancement of production facilities and equipment is directly related to the quality, reliability, and performance of the products produced by flexible PCB manufacturers.
How do flexible PCB manufacturers respond to the diversification and small batch of market demands?
Flexible PCB manufacturers can respond to the diversification and small batch of market demands in the following ways:
1. Flexible production processes: Flexible PCB manufacturers Establish production processes that can be quickly adjusted and switched to adapt to the production of flexible PCBs with different specifications and designs.
2. Flexible PCB manufacturers optimize inventory management: Stock some common raw materials and components to reduce the procurement time and cost for small batch orders.
3. Flexible PCB manufacturers invest in advanced manufacturing equipment: Adopt multi-functional and highly automated equipment that can be quickly converted between different small batch orders to improve production efficiency.
4. Flexible PCB manufacturers strengthen R&D capabilities: Be able to quickly develop and customize new products and solutions that meet diversified needs.
The R&D capability of flexible PCB manufacturers is a key factor for them to maintain competitiveness and achieve sustainable development in the market.
A flexible PCB manufacturers strong R&D capability is first reflected in the ability to closely follow the technological development trends of the industry and make early arrangements for the research and development of new technologies and processes. This includes the exploration and application of new materials, such as finding substrate materials that are more flexible, resistant to high temperatures, and have low loss; as well as the research on advanced manufacturing processes, such as more refined circuit etching techniques and higher-precision lamination processes.
Flexible PCB manufacturers with excellent R&D capabilities can quickly develop customized products based on market demands. They can work closely with customers, understand the unique application scenarios and performance requirements of the customers, and thereby design flexible PCB solutions that meet specific needs.
The innovation ability of the flexible PCB manufacturers R&D team is also crucial. They can propose novel design concepts and structures to improve the performance of flexible PCBs, reduce their size and weight, and enhance their reliability and durability.
In addition, the R&D capability is also reflected in the continuous optimization and improvement of products. By collecting market feedback and data from practical applications, the performance and quality of the products can be continuously improved to enhance the competitiveness of the products.
At the same time, Flexible PCB manufacturers an efficient R&D management system can ensure that R&D projects are completed on time, R&D costs are reasonably controlled, and R&D results are effectively transformed into actual production capacity and market benefits.
In conclusion, the R&D capability of flexible PCB manufacturers covers multiple aspects such as technology tracking, customized development, innovative design, product optimization, and R&D management. The comprehensive performance of these aspects determines the position and development potential of the manufacturers in the market.
5. Establish an efficient supply chain: Flexible PCB manufacturers establish close cooperative relationships with suppliers to ensure the timely supply of raw materials to meet the urgent needs of small batch production.
6. Adopt modular design: Decompose the design of flexible PCBs into modules, and meet different needs through the combination of modules to reduce the time and cost of redesign.
7. Digital management system: Flexible PCB manufacturers utilize information technology to achieve efficient management of production planning, scheduling, quality control, etc., and improve the response speed to diversified and small batch orders.
8. Flexible PCB manufacturers cultivate a multi-skilled workforce: Employees possess multiple skills and can be flexibly deployed among different production tasks to improve production flexibility.
9. Work closely with customers: Flexible PCB manufacturers understand customer needs in depth, make production preparations in advance, and shorten the delivery cycle.
10. Flexible PCB manufacturers provide sample and rapid prototyping services: Help customers conduct tests and validations in the early stage of product development to promote the generation of orders.
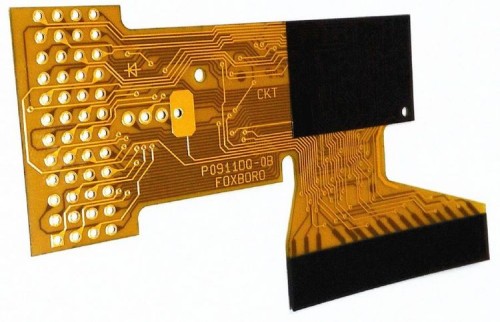
Flex PCB board materials selected by flexible PCB manufacturers.
Flexible PCB manufacturers typically select the following common flex board materials:
1. Polyimide (PI): It has excellent high-temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties, and is one of the widely used materials in flexible boards.
2. Polyester film (PET): It has a relatively lower cost but may have inferior performance compared to PI.
3. Liquid crystal polymer (LCP): It has advantages such as a low dielectric constant and low water absorption, and is suitable for high-frequency and high-speed applications.
Different materials vary in performance, cost, and application scenarios. Flexible PCB manufacturers usually choose the appropriate flexible board material based on specific product requirements and cost considerations.
Advantages and disadvantages of polyimide (PI)
Polyimide (PI), as a commonly used material for flexible PCB, has the following advantages:
Advantages:
1. Excellent high-temperature resistance: It can maintain stable performance in high-temperature environments and can withstand high processing and operating temperatures.
2. Good mechanical properties: It has high strength and flexibility and can withstand repeated bending and folding.
3. Strong chemical corrosion resistance: It has good tolerance to a variety of chemical substances.
4. Low dielectric constant and low loss factor: Suitable for high-frequency circuits with good signal transmission performance.
5. Excellent electrical insulation properties: It can effectively prevent short circuits and leakage in circuits.
Disadvantages:
1. High cost: Compared to some other materials, it is more expensive, increasing production costs.
2. Hygroscopicity: It may absorb a certain amount of moisture in a humid environment, affecting performance.
3. Difficult processing: Higher requirements for processing techniques and equipment.
Problems encountered in the application of polyimide (PI) in flexible PCB
In the application of polyimide (PI) in flexible PCB, the following problems may be encountered:
1. Thermal expansion coefficient issue: The thermal expansion coefficient of PI is relatively large. When experiencing temperature changes, it may lead to matching problems with other materials, thereby affecting the reliability and performance of the PCB.
2. Hole metallization difficulty: In the hole metallization process during PCB manufacturing, the chemical properties of the PI surface may cause difficulties in controlling the quality of the hole wall metallization, affecting the reliability of the electrical connection.
3. Surface flatness: The surface flatness of the PI film is sometimes not ideal, which may affect the subsequent circuit pattern production and the accuracy of fine lines.
4. Bonding performance: The bonding performance with the cover layer or other materials may not be ideal. Special treatment and adhesives are required to ensure good bonding.
5. High cost: As mentioned earlier, the PI material itself is expensive, which may increase the overall cost of the flexible PCB, especially in large-scale production where the cost pressure is significant.
6. Dimensional stability: In long-term use or under specific environmental conditions, dimensional changes may occur, affecting the accuracy and performance of the PCB.
When flexible PCB manufacturers make selections based on the performance of different PIs, they usually consider several key factors:
Firstly, Flexible PCB manufacturers see the operating temperature range. If the application scenario requires operation in a high-temperature environment, a PI material with higher high-temperature resistance performance needs to be selected.
Secondly, mechanical properties are considered by flexible PCB manufacturers, such as flexibility and resistance to bending fatigue. For flexible boards that need to be bent or folded frequently, a PI with excellent flexibility and fatigue resistance should be selected.
Flexible PCB manufacturers see the dielectric properties. For high-frequency applications, a PI with a low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss is needed to ensure good signal transmission.
Chemical stability is also a consideration by flexible PCB manufacturers. If the flexible board may come into contact with specific chemicals, then a PI material that can withstand the erosion of these chemicals needs to be selected.
In addition, flexible PCB manufacture cost cannot be ignored. A PI with better performance but high price may not be suitable for all products. Manufacturers need to balance performance and cost to meet market demands and cost budgets.
Finally, the supply stability and processability of the PI material will also be considered to ensure the smooth progress of the production process.