Description
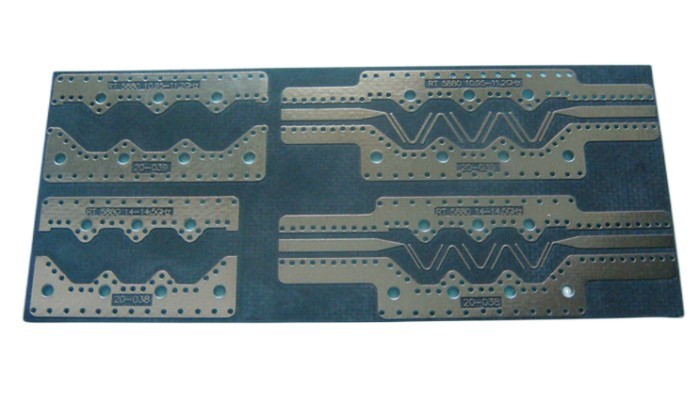
arlon pcb
Number of floors: 2
Plate thickness: 0.8 ± 0.1mm
Plate used:arlon
Dielectric constant: 2.55
Minimum hole diameter: 0.2mm
Surface treatment:plated gold
blue soldermask
Minimum trace width/distance: 0.2mm/0.2mm
Process characteristics: high-frequency materials,arlon
The differences between Arlon PCB and Rogers PCB are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- High-frequency performance: Rogers PCB materials have characteristics such as low dielectric constant, low loss factor, and low dielectric loss, endowing it with excellent performance in high-frequency signal transmission and being suitable for high-speed digital circuits, microwave communication, and other fields. While Arlon PCB materials also have specialized electrical, thermal, mechanical, or other performance characteristics, mainly used in wireless communication infrastructure, military and commercial avionics, and semiconductor testing and measurement equipment.
- Material characteristics: Arlon PCB materials have excellent mechanical properties, such as low dielectric loss, low signal loss, high thermal conductivity, and controllable impedance. Rogers PCB materials, on the other hand, have characteristics such as high thermal conductivity, high dielectric constant, excellent mechanical performance, and environmental protection performance.
- Application fields: Due to their different performance characteristics, Arlon PCB is often used in fields such as wireless communication, military and commercial avionics, and semiconductor testing; while Rogers PCB is widely used in fields such as aviation, aerospace, communications, automobiles, and consumer electronics, such as satellite communication systems, radar equipment, automotive electronic control modules, and so on.
In practical applications, the choice between Arlon PCB and Rogers PCB should be determined according to specific needs and application scenarios.