FR-4 PCB Manufacturing process-Drilling
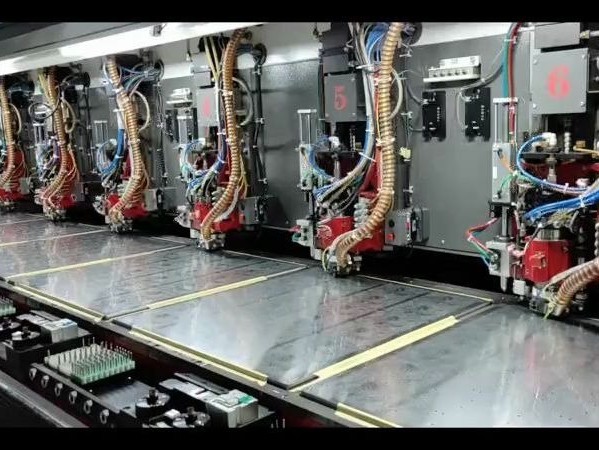
The drilling process in PCB manufacturing is a crucial operation, and its main purpose is to precisely create various types of holes on the PCB board, including vias, pad holes, and non-copper mounting holes (Npth). These holes play a key role in the PCB, used to achieve electrical connections between different layers, provide locations for component installation, or meet other specific functional requirements.The core objective of PCB manufacturing process drilling is to precisely drill the through-holes required for circuit connection between layers on the PCB surface. In this process, the main raw materials include drill bits, cover plates, and backing plates. Drill bits are usually composed of tungsten carbide, cobalt, and organic adhesives. The cover plate has multiple key functions during the drilling operation. It can provide precise positioning for the drill bit, effectively dissipate the heat generated during the drilling process, significantly reduce the occurrence of burrs, and prevent the pressure foot from causing damage to the board surface. The backing plate mainly plays the role of protecting the drilling machine table, can effectively prevent burrs at the exit, reduce the temperature of the drill bit, and clean the glue residue in the drill bit groove.

The types of PCB manufacturing process drilling are diverse, mainly including vias, pad holes, and non-copper mounting holes (Npth). Vias mainly play the role of electrical conduction and do not need to be used for component insertion and soldering. The surface treatment methods can be window opening (exposing the pad), covering with oil, or plugging with oil. Pad holes are designed specifically for the pins that need to be inserted and soldered for components, and the surface of the pad must remain exposed. Non-copper mounting holes (Npth) are usually screw holes or holes for the plastic fixing feet of components. These holes do not have electrical performance and mainly play the role of positioning and fixation.
In PCB design, factors such as the spacing between vias and the spacing between pad holes have a significant impact on the PCB production drilling process. If the distance between two holes is too close, it will bring many challenges to the PCB production drilling process, such as easily causing drill bit breakage, resulting in an unsightly chipped hole on the PCB or a missed drilled hole causing circuit non-conduction.
In conclusion, the drilling process holds a pivotal position in the PCB manufacturing process. Factors such as the accuracy of drilling and the smoothness of the hole wall are directly related to the electrical performance and signal integrity of the PCB, exerting a profound influence on the overall quality and performance of the PCB.
How is the accuracy of PCB drilling controlled?
The accuracy of PCB manufacturing drilling is mainly controlled through the following methods:
1. Advanced drilling equipment: Adopting high-precision and high-stability CNC drilling machines that can precisely control the position, depth, and aperture of the drilling.
2. High-quality drill bits: Selecting high-quality, precisely sized, and wear-resistant drill bits to reduce aperture deviations caused by drill bit wear.
3. Precise positioning system: Through advanced visual positioning or mechanical positioning systems, ensure the accurate position of the PCB board during the drilling process.
4. Reasonable drilling parameter settings: Including rotational speed, feed speed, and retraction speed, etc., which are optimized and adjusted based on the material and thickness of the PCB board to ensure drilling accuracy.
5. Strict equipment maintenance: Regularly calibrate, maintain, and repair the drilling equipment to ensure its stable performance and reduce accuracy errors caused by equipment aging or malfunctions.
6. Control the processing environment: Maintain a stable temperature and humidity to avoid the influence of environmental factors on the PCB board and equipment accuracy.
7. Pretreatment before drilling: Such as flattening the PCB board to ensure its surface flatness, which is beneficial for improving drilling accuracy.
8. Quality inspection and feedback: During or after the drilling process, the drilling accuracy is inspected through professional inspection equipment. Deviations are detected and corrected in a timely manner. At the same time, the inspection results are fed back to the production process to adjust and optimize the process parameters.